Urology Worldwide: Best Hospitals, Doctors, Options, & Cost
Urology is a subspecialty of surgery that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions and diseases related to the urinary tract in both men and women and the male reproductive system. Common conditions treated by urologists include incontinence, urinary tract infections, prostate problems, erectile dysfunction, male infertility, kidney stones, and kidney cancer.
Urology doctors use various diagnostic tools and techniques to diagnose these conditions. Once a diagnosis has been made in the clinic, urologists can offer multiple treatment options. The field of urology is constantly rising, with technologies and treatments being developed all the time.
Urology is an essential field of medicine critical to improving health and quality of life. At AiroMedical, we're ready to investigate your situation and devise solutions: the doctor and the clinic.
Best urology hospitals worldwide
What helps to find the best urology hospital?
Selecting a suitable urology hospital abroad requires careful consideration of several factors. The clinic’s reputation, experience, and success rates in treating urology conditions are crucial. Equally important is the medical staff’s expertise.
In addition, the hospital should have access to the latest technology and equipment. Patient reviews can provide valuable insight into the quality of care. Certifications are indicators of the urologists' competence. The urology hospital or clinic should also offer the latest treatments, such as laser enucleation and robotic surgeries.
Other essential factors include cost, location, and language and cultural considerations. A hospital with a narrow specialization in urology, such as urologic oncology, can offer expert care. Considering these factors can help you find the best clinic for your needs.
Top rated urologists worldwide
How to select the best urologist?
Finding the best urologist when you need such help looks complex, but it is real. Check our simple tips for successful urologist findings. Look at their reputation and expertise in specific urological conditions. The best ones have lots of experience in urology and perform various procedures, from simple to complex and robot-assisted surgeries.
Top-rated urology doctors provide patient care and handle sensitive urology issues. They use the latest diagnosis and treatment tools and excel in non-surgical and surgical urology treatments. Doctors help guide your recovery and give advice to prevent any complications.
World-renowned physicians work as a team and base their work on scientific research, and are good at explaining information clearly. Looking for such a urology specialist may seem challenging; however, AiroMedical and our rating and booking system will help. Whether you are looking for the best urologist in the world or just a proper doctor near you, our system will guide you.
Latest urological diagnostic tools
A urinary tract diagnosis typically includes a range of tests and assessments to diagnose various conditions in urology.
A skilled doctor and a reputable urology clinic or hospital are crucial because a correct, timely diagnosis can lead to the proper treatment, improved patient outcomes, and a lower risk of complications.
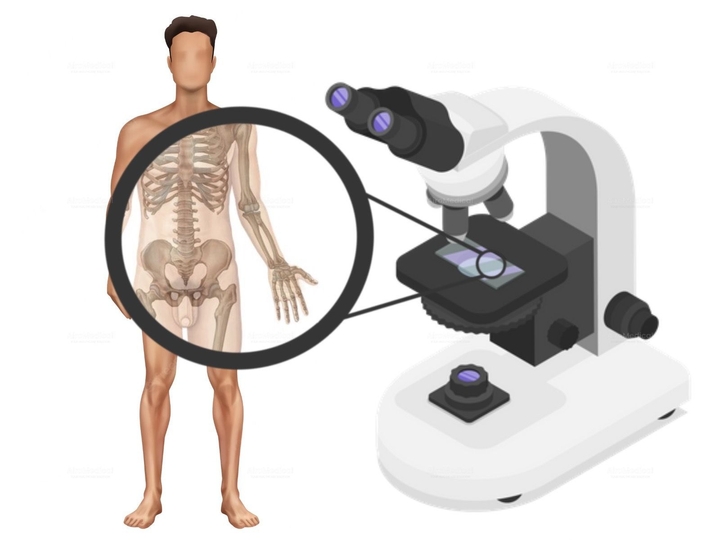
Conventional methods
In addition, experienced professionals can offer personalized care and advice, further enhancing the effectiveness of urology treatments and overall patient satisfaction.
More advanced options
These tests and methods in urology may vary depending on the individual's symptoms and the suspected underlying condition. Here are a few more ways that are used in every modern hospital:
These methods may be used in the hospital alone or in combination, depending on the specific urological condition and the individual's symptoms.
Top offers
Advanced treatment solutions in urology
The term "advanced treatment solutions" in urology refers to the newest and most advanced ways to treat different urological conditions in the hospital. There are several types of urology treatments abroad. Here are some of these:
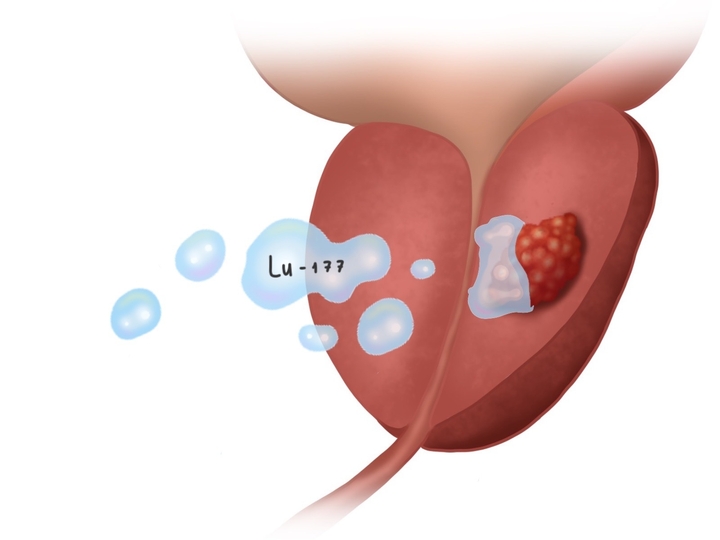
Latest treatment options
These are some examples of how treatments in a urology clinic or hospital can be done. It will depend on the person's current health, medical history, expectations, prognosis, etc.
Men’s health & cosmetics
These treatments, available at every prestige urology clinic, aim to boost men's physical health and self-esteem, enhancing their quality of life. Skilled urologists focused on improving men’s wellness perform them.
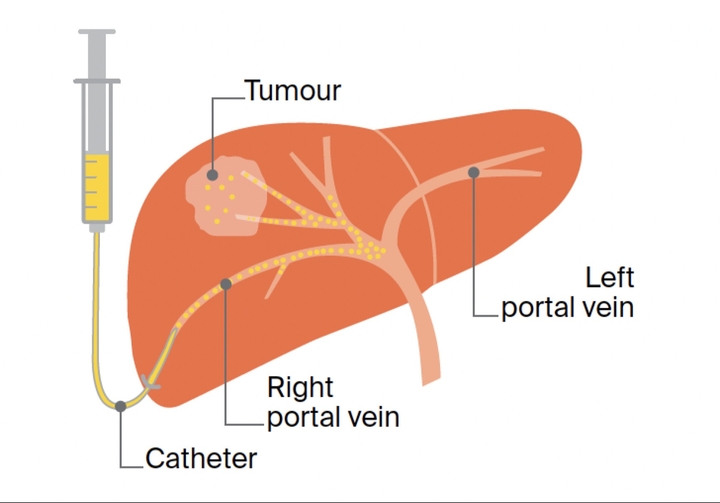
More advancements in urology care
These are some of the more advanced ways to treat conditions in urology. Of course, the treatment choice will depend on the situation, hospital, and budget. Here are a few more ways:
At the AiroMedical platform, we're committed to staying updated with the latest advancements in urology and choosing the best healthcare provider. We aim to make new, effective urology treatments accessible to our patients. Our team researches and includes innovative procedures in our packages, ensuring that our customers receive top-quality care no matter where they travel for their medical needs.
Urology treatment cost worldwide
Advantages of medical tourism
AiroMedical is a medical tourism provider that offers various benefits for patients seeking urological treatments abroad. We use comprehensive statistics and annual reports to identify each reputable urology clinic and hospital globally.
Benefits to exploring medical travel for urology care
Based on years of experience, we can summarize them as follows:
Some of the reasons to make a request
AiroMedical provides all listed above and more to patients seeking urology in the clinic abroad. Let’s go to the recovery together.
How AiroMedical can help you
Read more in our blogs
FAQ
Who are the best doctors for Urology?
Prof. Dr. med. Jürgen Gschwend from
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Martin Kriegmair from
Urological Clinic Munich-Planegg
Dr. med. Nathan Kaminski from
Urology Practice Wiener Platz Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Michael Siebels from
Urological Clinic Munich-Planegg
Prof. Dr. med. Johannes Ullrich Schwarzer from
Urological Clinic Munich-Planegg