Neurosurgery (Brain Surgery) Worldwide: Best Hospitals, Doctors, Options, & Cost
Neurosurgery can be a complicated and demanding field because it has many challenges. The nervous system anatomy is very delicate. Even small mistakes in brain surgery can affect a patient’s health and personality. Some neurosurgery procedures require a long time to recover. The patient may be at risk for complications and need much therapy and rehabilitation.
Neurosurgery doctors must keep up with the rapidly changing technology. New surgical tools and techniques, imaging modalities, and computer-assisted surgery exist. Doctors often deal with patients in poor condition after brain surgery and have to make decisions that can affect their lives.
Access to neurosurgery care and top neurosurgeons is limited in some parts of the world, making it hard for people with neurological conditions to get the help they need. We at AiroMedical, despite the difficulties, are ready to find the solution for your case.
Best neurosurgery hospitals worldwide
Tips for finding the right brain & spine surgery center
Here are some steps to ensure you get the best treatment in neurosurgery. First, consider centers with specific expertise to find experienced and specialized healthcare providers. Choose a hospital or clinic with more surgeries for a more significant experience. Look for high success rates in brain surgery or other neurosurgery procedure. Opt for the latest, most effective technologies like neuronavigation and laser ablations.
Second, ensure that the neurosurgery doctor has national and international certifications to the adherence to the best quality standards. Look for patient reviews that show the hospital's reputation, the competence of its healthcare professionals, and the overall patient experience.
Third, consider a neurosurgery center with a convenient location. And evaluate the treatment cost and available payment arrangements. Considering all listed above will help you make an informed decision and increase your confidence and likelihood of better treatment results.
Top brain & spine surgeons worldwide
How to select the right neurosurgery specialist?
Choosing the right neurosurgeon is a vital decision. The best neurosurgeon in the world would be an expert in a specific neurology area and hold relevant certificates from trusted organizations. They'd demonstrate high success rates and a safe record, employing the latest technology, such as neuroimaging for precise diagnosis and minimally invasive surgery for patient safety.
A famous neurosurgeon would have extensive experience and a portfolio of scientific works, showing their commitment to evidence-based medicine. They would foster a multidisciplinary approach, collaborating with other medical experts for comprehensive patient care. The best brain surgeons prioritize patient care and understand neuroplasticity, helping patients recover optimally.
But remember, the top neurosurgeon for you fits your specific needs, has the necessary experience, and makes you feel at ease.
Neurosurgery diagnosis
Getting a neurosurgery diagnosis abroad can be tricky, but these will help. Look for a neurosurgeon who is an expert in the condition you need help with. To realize “the best neurosurgery in the world” is complex but accurate.
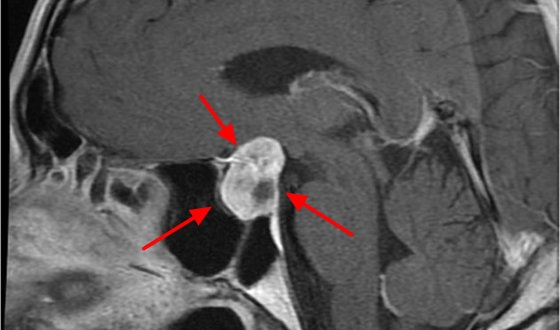
Bring your medical records and test results to the doctor's office. These can help the doctor determine what's wrong and what neurosurgery treatment to offer. Be ready for imaging scans (CT, MRI, PET-CT), blood tests, and other diagnostic procedures needed in the clinic to diagnose accurately.
Concerning the diagnostic done in the best clinics
These are just a few ways that neurosurgery can use advanced diagnostic tools. This help to make more accurate diagnoses, create a more precise neurosurgery treatment plan, and perform more successful brain surgery. For a correct diagnosis, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and other fluids and tissues must be tested in a lab in the clinic.
With these tools, neurosurgery specialists can see detailed pictures, which helps them figure out what's wrong and plan how to treat it in the hospital.
If you're unsure about the diagnosis or treatment plan, it's best to talk to another qualified neurosurgeon in a reputable hospital.
After the necessary tests are done, the medical team makes a diagnosis and recommends a treatment plan, which may include more than one protocol. Neurosurgery’s current ways of diagnosing and treating disorders make it possible to find them early and start neurosurgery care immediately.
Top offers
Advanced treatment solutions in neurosurgery
Functional neurosurgery, stereotactic radiosurgery, and endoscopic brain surgery are all more advanced ways to do brain surgery worldwide. High-tech tools like computer-assisted navigation, microscopy, and endoscopy help to make brain & spine interventions more accurate.
New techniques used in leading neurosurgery centers
Some brain, nerve, or spine diseases require unique options available only in specific locations or clinics. It is even more actual for brain cancer which urges for the best approach. Explore more methods that result in fewer complications and a higher success rate.
Other methods applied for brain and spine issues
These are just a few of the many ways advanced brain surgery can treat problems with the brain. At AiroMedical, we do extensive research & development to explore the best treatment options for each neurosurgery case.
Our tools include extensive scientific research databases like NCBI, human expertise, and AI tools. Searching, booking, and checking your next brain and spine surgery with AiroMedical makes world-class clinics and doctors available to everyone.
Neurosurgery treatment cost worldwide
Neurosurgery€250 - 412,540
Advantages of medical tourism
Getting brain surgery outside your home city or country is getting increasingly popular. Patients search for the latest surgical approaches and qualified specialists. In addition, we analyzed the primary factors driving patients to think about having neurosurgical intervention abroad.
Why consider medical travel for brain surgery?
It's essential to note that while medical tourism can provide many benefits, some risks also must be considered. To do thorough research, choose a reputable and accredited neurosurgery hospital and clearly understand the procedure's risks, benefits, and potential complications before deciding.
Also, it's crucial to know the laws and regulations of the country you intend to travel to and ensure that you have the appropriate insurance coverage for neurosurgery. Communication with your surgeon before and after the neurosurgery is crucial to ensure a smooth recovery process.
AiroMedical is ready to provide all benefits and protects clients from risks from the first request to recovery after the neurosurgery treatment.
How AiroMedical can help you
Read more in our blogs
FAQ
What are the best clinics for Neurosurgery?
Who are the best doctors for Neurosurgery?
Prof. Dr. med. Alexander Muacevic from
European Radiosurgery Centre Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Harald-Robert Bruch, MSc, PhD from
Oncological and Haematological Praxis Clinic Bonn
Prof. Dr. med. Bettina Kuschel from
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Bernhard Meyer from
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Bernhard Hemmer from
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich