Colon cancer treatment Worldwide: Best Hospitals, Doctors, Options, & Cost
Colon cancer remains the second top cause of cancer-related deaths globally. According to WHO statistics, over 1.9 million new cases were diagnosed in 2020, resulting in more than 930,000 deaths. The risk rises with age, and most are diagnosed after 50.
Early detection and the start of colon cancer treatment are paramount, as many individuals may not have symptoms in the initial stages. The good news is that in high-income countries, the incidence rates have declined, thanks to screening programs. A 10-yearly colonoscopy is the most effective, with a reduction of death in 73%. Colon cancer treatment prognosis varies based on the stage at diagnosis. For example, 5-year life expectancy in the first stage is 91%. Still, it is only 12-14% in stage 4, so proper colon cancer treatment is crucial.
Best colon cancer treatment centers
Colon cancer hospital selection
Selecting the ideal hospital for colon cancer treatment is a critical decision that demands thorough research due to the disease's complexity. The best centers have a multidisciplinary team of experts, from colorectal surgeons to dietitians, ensuring a holistic treatment approach.
Advanced diagnostic tools, adherence to international standards, and surgical and non-surgical colon cancer staging treatment, including the latest immunotherapy, are hallmarks of top-rated hospitals. Comprehensive rehabilitation, encompassing dietary guidance, physical therapy, and emotional support, is vital for holistic recovery. A hospital's reputation is also crucial, informed by reviews and track records regarding success rates and patient satisfaction. Proximity and affordability are practical considerations.
Ultimately, the best choice balances quality care, accessibility, and cost. AiroMedical is committed to assisting patients in navigating this decision, prioritizing their well-being.
Top colon cancer doctors
About your colon cancer doctor choosing
When facing a diagnosis, selecting the right colon cancer specialist is paramount. The ideal colon cancer doctor possesses specialized oncology training, particularly in colon cancer, and is affiliated with esteemed medical organizations, signifying their dedication to excellence and adherence to high standards.
Effective treatment often involves a collaborative approach, with doctors teaming up with various specialists to provide comprehensive care. These professionals use advanced diagnostic tools to ensure accurate cancer staging, crucial for tailored treatment plans. Their vast experience, reflected in their success metrics, offers reliability. They also prioritize patient safety, closely monitoring for any treatment-related complications. Actively participating in research, each reputable colon cancer doctor brings the latest treatments to the patients. A holistic approach, encompassing medical and therapeutic strategies, ensures overall well-being.
Patient testimonials offer insights into a colon cancer doctor's approach and effectiveness. AiroMedical can help you navigate this selection process, connecting with your top colon cancer doctor from our extensive database.
Top offers
Treatment of colon cancer
The best colon cancer treatment choices are influenced by the cancer's type and stage, potential side effects, and the patient's health and preferences. When deciding on a treatment, it's also important to consider any other medications the patient is on, their nutritional status, potential treatment side effects, and support system.
Surgical solutions
Surgery is a primary treatment for colorectal cancer, especially for those seeking stage 1 colon cancer treatment. The process entails taking out the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue.
- An open colectomy. During open surgery, the surgeon creates a sizable incision in the abdomen to extract the tumor and a portion of the healthy colon or rectum. The segment containing the cancer and the connected lymph nodes are also taken out.
- Laparoscopic-assisted surgery. This minimally invasive procedure involves small incisions and specialized instruments. It's beneficial for early stages, as effective as traditional surgery, but often with a quicker recovery time.
Ten years post-surgery, both laparoscopic and open colectomy procedures for cancer show comparable survival and recurrence rates. The disease-free survival rates stood at 45.2% for the laparoscopy and 43.2% for the open surgery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays, like X-rays, to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is frequently used for rectal cancer but can also be applied to colon cancer in specific cases. Radiation is used for colon cancer treatment before or after surgery, often in conjunction with chemotherapy, to manage tumors, address metastasis, or alleviate severe symptoms.
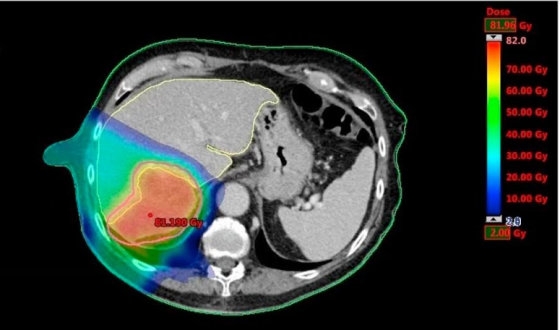
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is an advanced form of 3D-CRT. The radiation varies in intensity across areas, giving different doses to parts of the tumor or nearby tissues. This precision helps reduce damage to healthy tissues and is beneficial for treating tumors close to critical structures. The 12-month overall survival was 95%, while the 5-year it was 86%.
- Endocavitary radiation therapy: A device in the rectum delivers high-intensity radiation in short bursts—suitable for small tumors or recurring cancers post-radiation.
- Interstitial brachytherapy: A tube placed into the tumor receives radioactive pellets. It's for patients unfit for surgery or with recurring rectal cancer.
The CyberKnife system is a type of SBRT that uses real-time imaging to track the tumor's movement and adjust the radiation beams accordingly. It's particularly effective for treating small, well-defined tumors. After one year, local control was 83.8%, and progress-free survival was 55%.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of anti-cancer drugs administered either intravenously or orally. These drugs circulate throughout the body, eliminating cancer cells. Chemo is a standard in colorectal cancer treatment and can be used in various cases as:
Chemo drugs for colon cancer treatment can be given as short injections or more prolonged infusions in medical settings. Central venous catheters like ports or PICC lines are often used for administration.
Treatment typically follows cycles, allowing recovery time between drug doses. The duration and frequency depend on the specific drug. Adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemo usually lasts 3 to 6 months, while treatment length for advanced cases varies based on effectiveness and side effects.
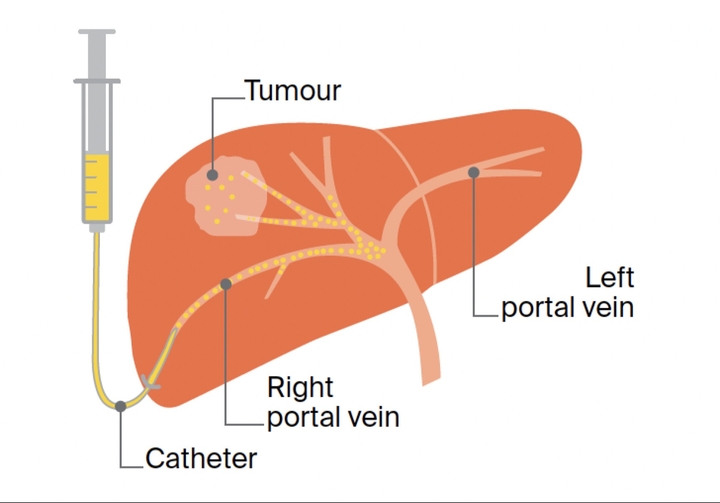
Drugs are introduced intravenously or orally into the bloodstream, reaching most body parts during systemic chemotherapy. They can target a specific body area, like the hepatic artery, for liver metastases as regional chemo.
The most used chemo in colon cancer treatment: 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU), Capecitabine (Xeloda), Irinotecan (Camptosar), Oxaliplatin (Eloxatin), Trifluridine and tipiracil (Lonsurf).
These drugs are often combined in specific protocols to enhance their effectiveness, and sometimes, they're paired with targeted therapy drugs to improve the results of colon cancer treatment.
Each protocol has its specific use cases, benefits, and side effects. The choice of regimen often depends on the disease stage, the patient's health, and other factors.
Targeted therapy
Targeted treatment for colon cancer focuses on specific cell changes causing cancer. Unlike chemotherapy, targeted drugs often work when chemo doesn't and have distinct side effects. They can be used alongside chemo or independently if chemo fails. These drugs circulate throughout the body, making them especially effective against metastasized cancers.
While these therapies offer a more precise approach to treating colorectal cancer, it's essential to monitor and manage side effects under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a treatment that boosts the body's immune system to fight colorectal cancer. They aid the immune system in identifying and combating cancer cells.
These medications focus on particular proteins in immune cells that stop the immune system from targeting the body's cells. The drugs amplify the immune response against cancer cells by inhibiting these checkpoints. Here are some drugs for colon cancer treatment:
For colon cancer treatment, several types of vaccines have been explored: autologous, peptide vaccines, dendritic cell (DC) vaccines, viral vector vaccines, and oncolytic virus therapy.
Colon cancer treatment by stage
Colon cancer staging and treatment are crucial for understanding and managing the disease. Each stage has specific treatment protocols, ensuring the best chance of recovery.
Chemotherapy might be recommended in cases of recurrence risks. For patients without high-risk features, options include check-ups or 6-month treatments with 5-Ftuorouracil, leucovorin, and capecitabine. The protocols like FOLFOX or CapeOx are used for high-risk patients.
Operation alone has an almost 60% success rate with a 35.2% recurrence rate; surgery+chemo demonstrates 83.4% and 18.1%, respectively, due to the study.
Treatment for stage 4 colon cancer encompasses a range of interventions.
- Surgical procedures can involve local excision, resection, and sometimes removal of parts of organs like the liver, lungs, and ovaries where the cancer has metastasized. In addition, advanced methods like HIPEC surgery can be considered.
- Chemotherapy, such as FOLFOX and FOLFIRI, controls cancer growth and spread.
- Targeted therapies, like Bevacizumab and Cetuximab, focus on specific cancer cell attributes or their environment.
- Immunotherapy, including Pembrolizumab, boosts the body's natural defenses against cancer.
- Radiation therapy, including techniques like CyberKnife, aims to shrink tumors, while ablation and embolization methods, including TACE, destroy or block tumors.
- Lastly, palliative care prioritizes patient comfort and symptom management.
Treatment for metastatic colon cancer is multifaceted, aiming to control the disease and maintain the patient's quality of life. Regular consultations with oncologists ensure the treatment plan is tailored to the patient's needs.
Cost of colon cancer treatment
Colon cancer€250 - 412,540
Advantages of medical travel
The global healthcare landscape is evolving, with many patients considering international medical needs options. For patients seeking colon cancer treatment abroad, numerous advantages can be offered.
The key benefits of international colon cancer treatment
At AiroMedical, we connect patients and world-class medical facilities. Our services go beyond just coordinating treatment; we handle all logistical aspects, from travel arrangements to post-treatment care.
We believe quality healthcare should be accessible to all, regardless of borders. Reach out to us, and embark on your treatment journey with assurance and support.
How AiroMedical can help you
Read more in our blogs
FAQ
What are the best clinics for Colon cancer?
Who are the best doctors for Colon cancer?
Prof. Dr. med. Thomas Vogl from
University Hospital Frankfurt am Main
Dr. med. Anett Tillmann, MBA from
Bundeswehr Hospital Berlin
Prof. Dr. med. Roland Ladurner from
Martha-Maria Hospital Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Alexander Muacevic from
European Radiosurgery Centre Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Harald-Robert Bruch, MSc, PhD from
Oncological and Haematological Praxis Clinic Bonn