Esophageal cancer treatment Worldwide: Best Hospitals, Doctors, Options, & Cost
Esophageal cancer is a major global health concern, with more than 500,000 new cases recorded annually. The overall survival rate stands at roughly 20% after five years, and most patients are diagnosed when the disease is already in its advanced stages, making esophageal cancer treatment for stage 3 or 4 particularly challenging. However, when detected early, the five-year survival rate can reach up to 47%. Unfortunately, only a small fraction of these cases are identified at such an early stage.
Thus, strategies to combat this disease focus on early detection and research into new esophageal cancer treatment techniques. In addition, having a proper clinic & doctor that helps to cope with esophageal tumors is essential.
Best esophageal cancer centers
Selecting the esophageal cancer treatment hospital
When asking for the best hospital for esophageal cancer treatment, it is important to consider expertise, technology, adherence to industry guidelines, surgical and endoscopic options, availability of advanced therapies, rehabilitation services, and success rates. The center or clinic should have a diverse team of experts who use advanced diagnostic techniques and adhere to international guidelines.
The center should offer a range of surgical techniques, including minimally invasive and robotic-assisted procedures and endoscopic treatments. The availability of advanced therapies in the hospital, like targeted therapies, radiation oncology, and immunotherapy, is essential. Post-treatment support, including swallowing rehabilitation, is key.
Additionally, high success rates indicate a commitment to quality care. Considering practical aspects like location, cost, and hospital for esophageal cancer treatment, reputation is equally important. AiroMedical is ready to assist you in this process.
Top esophageal cancer doctors
Esophageal cancer doctor choosing
Choosing an esophageal cancer doctor is a significant step, requiring careful evaluation. Look for professionals specializing in oncology, gastroenterology, and thoracic surgery, particularly those skilled in minimally invasive and robotic surgeries.
Membership in esteemed organizations like ESMO and ESSO indicates their commitment to quality care and staying updated with medical progress. A strong record of successful treatments, advanced diagnostic methods usage, and a multidisciplinary team approach further boost the profile of the esophageal cancer doctor you consider choosing. Doctors active in research with strong patient testimonials enhance their credibility.
In addition, clear communication, patient understanding, and a comforting environment are crucial. The location also matters in striking a balance between quality care and accessibility. AiroMedical can assist in locating an esophageal cancer doctor best suited to your specific needs.
Top offers
Treatment of esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer treatment is a comprehensive, customized procedure that employs various techniques adjusted to the patient's health, cancer stage, and location. The primary strategies for esophageal cancer treatment include surgery (mostly for early-stage esophageal cancer treatment), radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy and their combinations.
Esophageal cancer treatment surgery
Operation is the most used first-line treatment for some types of esophageal cancer, with the methods depending on the stage and location of the tumor.
- The transhiatal approach involves a neck incision to remove most of the esophagus and a bit of the stomach, then connecting the remaining stomach to the leftover esophagus.
- The Ivor Lewis method of esophageal cancer surgical treatment requires cuts in the abdomen and chest to remove a section of the esophagus and click a part of the stomach to the chest's remaining esophagus.
- The thoracoabdominal approach is used for lower esophagus or junction tumors. It involves cutting from the abdomen to the left chest, dividing the esophagus, and linking the stomach or small intestine to the left chest to create a new pathway. Survival rates depend on the cancer stage but generally fall 30% at 5 and 20% at 10 years.
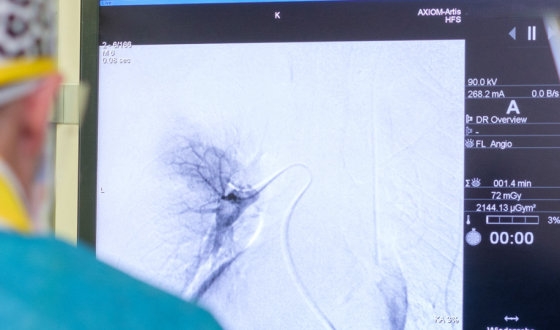
There's also an ablation, heat to clot blood, and endoscopic hemostatic clip placement, which uses small clips to close the bleeding vessel. Argon plasma coagulation is another method that uses argon gas and electricity to halt bleeding. Lastly, catheter embolization blocks the tumor's blood supply. In rare cases, surgery may be used to control the bleeding.
The choice among these procedures will depend on the cancer location, the patient's overall health, and the stage.
Radiation therapy
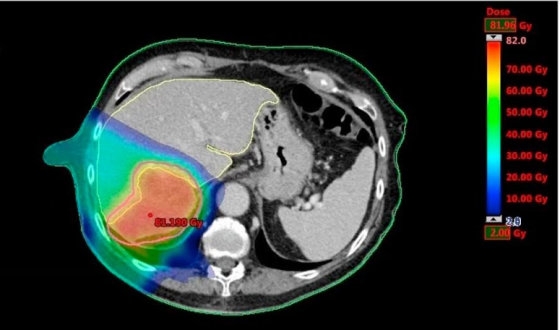
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles and is a powerful tool in esophageal cancer treatment. It can be used as the primary method for smaller cancers. Also, it can be performed post-operatively to destroy remaining cancer cells or combined with chemotherapy to shrink larger tumors before surgery. It's also applied in advanced stages and cases of cancer recurrence.
The duration and frequency of the procedures depend on why the radiation is needed and other considerations. The esophageal cancer treatment can take a few days to several weeks. When used solely, radiation therapy leads to a survival rate of around 18% after 1 year and less than 5% after 5 years for patients with stages I-III.
The one-year overall survival rate for esophageal cancer patients undergoing brachytherapy was 19.4%, with dysphagia-free survival at 28.9%, and the treatment showed the best outcome compared to other esophageal cancer stage 4 treatment methods.
Studies have shown that this method can control cancer growth in 92.4% of cases. The Gamma Knife treatment doesn't involve any surgical incision or long recovery time, making it a great way to manage esophageal cancer that has spread to the brain.
With this treatment, according to the study, about 67% of patients live for 3 years, and 56% live for 5 years. Survival rates are higher for earlier stages of cancer, from 79.3% for stage I, 66.3% for stage II, 43.2% for stage III, and 28.3% for stage IV.
Chemotherapy treatment for esophageal cancer
Chemotherapy can enhance the effectiveness of cancer treatment for esophageal cancer. It may be used before (neoadjuvant) or after (adjuvant) surgery to kill remaining cancer cells or make the tumor more susceptible to radiation. In some cases, it can be used for advanced stages.
Chemoradiation
Combining chemo and radiation therapy is widely used in cases where cancer has spread or recurred. Chemotherapy damages cancer cells, making radiation therapy more effective. For squamous cell esophageal cancer, chemoradiotherapy is commonly recommended as the first-line treatment. Surgery may be used afterward, depending on the results. Recent studies show using chemoradiotherapy before surgery is better than surgery alone.
It's commonly used for stage IB- III and sometimes stage IVA esophageal cancer. It has shown promising results in increasing the chances of completely removing the tumor. After checking up on patients for an average of 84 months, it was found that 44% of the group who had chemoradiation before surgery didn't see their cancer progress for five years.
It's been effective in controlling cancer growth and relieving symptoms. The complete response and survival rates for three and five years were 62%, 47%, and 37%, respectively. Any immediate harmful effects were able to be effectively managed.
Immunotherapy
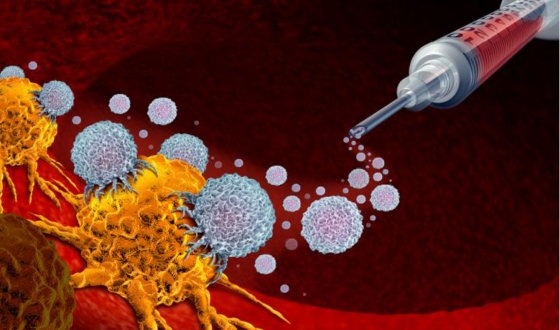
Immunotherapy is used in esophageal cancer treatment, leveraging the body's immune defense to fight cancer cells. Unlike chemotherapy, immunotherapy tends to involve fewer severe side effects.
Moreover, using Keytruda with chemotherapy reduced the chance of the disease worsening by 35% compared to chemotherapy alone. Trials (CheckMate 648, ESCORT-1st, KEYNOTE-590) suggest the combination has similar severe adverse event rates.
Targeted therapy
Targeted drugs address specific cancer cell changes. Esophageal cancer treatments such as Trastuzumab and Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan target HER2 protein on esophagus cancer cells but can cause side effects like severe heart and lung damage. Ramucirumab slows cancer growth by blocking new blood vessel formation, while Entrectinib and Larotrectinib target abnormal gene fusion. Overall response rates of targeted treatment vary from 32% to 68%.
Alternative treatment for esophageal cancer
Alternative treatments for esophageal cancer should not replace conventional methods like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy but can complement them. These complementary therapies include esophageal cancer natural treatments like acupuncture, mind-body therapies (meditation, yoga, tai chi), massage therapy, nutrition therapy, exercise, aromatherapy, music therapy, art therapy, hypnosis, and certain herbal or dietary supplements. They can help manage symptoms, reduce stress, improve mental and physical well-being, and manage the side effects of primary treatments.
The selection of esophageal cancer treatment depends on various factors, including the form, location, and stage of cancer, the patient's overall health, potential side effects, and personal preferences. Treatment often involves a multi-modality approach to provide the most effective strategy. Discussions with the healthcare team are essential for choosing the best treatment for esophageal cancer.
Cost of esophageal cancer treatment
Esophageal cancer€250 - 412,540
Advantages of treatment abroad
Medical tourism is gaining popularity as patients worldwide seek the best care for conditions like esophageal cancer. Going abroad for esophageal cancer treatment can offer several benefits:
Why check medical travel for esophageal cancer?
Summarizing, when diagnosed with esophageal cancer, it's vital to consider all possible treatment benefits. Medical tourism is a valuable resource, offering access to potentially life-saving treatments, renowned specialists, and cutting-edge technology that might not be available or affordable locally.
At AiroMedical, we facilitate your journey towards better health by linking you with prestigious medical facilities worldwide, ensuring you receive the best esophageal cancer treatment. Our services span the entire process, from identifying the ideal medical destination and coordinating your treatment plan to managing travel arrangements. Geographical boundaries should not restrict your treatment options. Connect with AiroMedical today and explore a world filled with healthcare opportunities.
How AiroMedical can help you
Read more in our blogs
FAQ
What are the best clinics for Esophageal cancer?
Who are the best doctors for Esophageal cancer?
Prof. Dr. med. Thomas Vogl from
University Hospital Frankfurt am Main
Dr. med. Anett Tillmann, MBA from
Bundeswehr Hospital Berlin
Prof. Dr. med. Roland Ladurner from
Martha-Maria Hospital Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Alexander Muacevic from
European Radiosurgery Centre Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Harald-Robert Bruch, MSc, PhD from
Oncological and Haematological Praxis Clinic Bonn