Radioiodine therapy Worldwide: Best Hospitals, Doctors, Options, & Cost
Update: Mar 06, 2026
Best hospitals for radioiodine therapy worldwide
Top doctors for radioiodine therapy worldwide
Top offers
Cost for radioiodine therapy worldwide
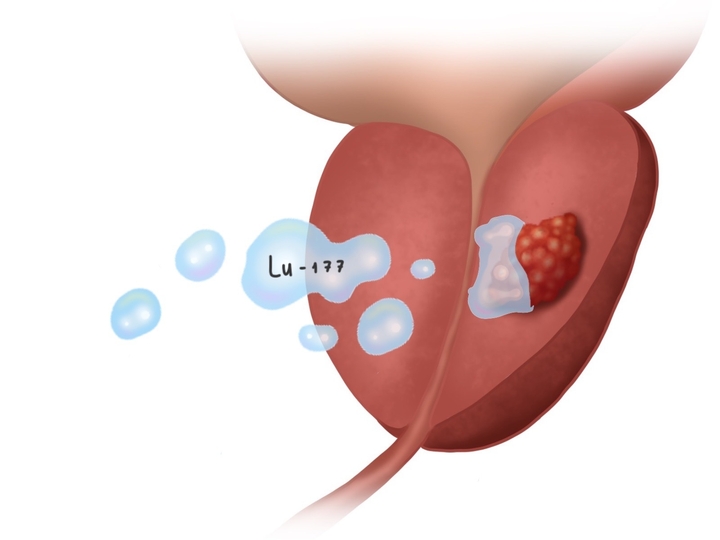
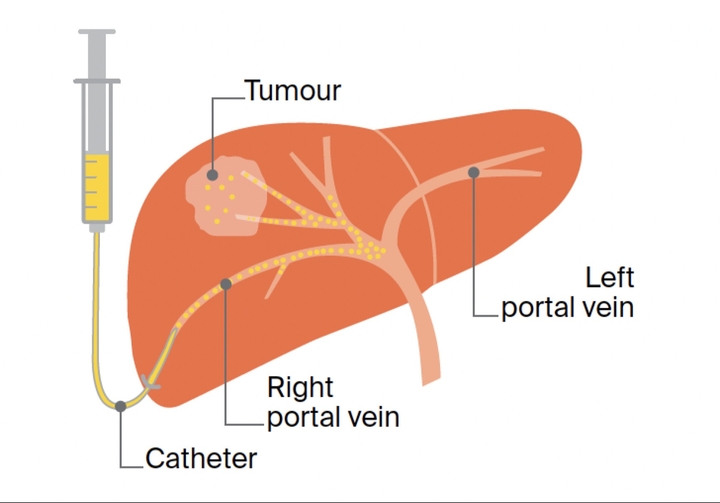
Radioiodine therapy€6,210 - 17,510
How AiroMedical can help you
Global medical travel platform for searching and booking treatments.
Read more in our blogs
FAQ
What are the best clinics for Radioiodine therapy?
Who are the best doctors for Radioiodine therapy?
Prof. Dr. med. Wolfgang Weber from
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Hans-Jürgen Biersack from
Beta Clinic Bonn
Prof. Dr. med. Peter Bartenstein from
University Hospital Ludwig-Maximilians Munich
Prof. Dr. med. Stefan Dresel from
Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch
Dr. med. Ingo Benz from
PAN Clinic Cologne